中央研究院 生物化學研究所
中央研究院 生物化學研究所
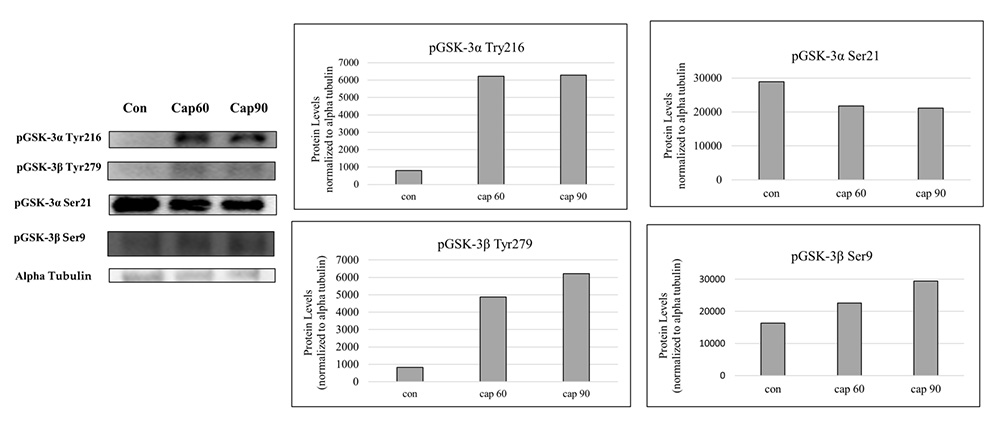
L. barbarum is a Chinese herbal medicine used to treat male infertility. The aim of this study was to investigate glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) phosphorylation involving sperm capacitation and the mechanisms by which L. barbarum polysaccharide (LBP) mixtures protect sperm. During capacitation at 60 or 90 min, the level of the sperm GSK-3 pTyr216/279 phosphoprotein significantly increased, whereas the levels of GSK-3 pS21 decreased but those of pS9 increased significantly. Treatment with 2 mg/mL LBP3M without exposure to iron slightly increased pGSK-3α S21 toward capacitation but significantly decreased pGSK-3α S9. The ability of 4 mg/mL LBP3M to prevent insults from 40 μM iron and exert posttranslational effects on sperm proteins was tested. Without iron insult, the relative phosphorylation of GSK-3 at pTyr216/279 significantly increased threefold after 60 min of incubation with 2 mg/mL LBP3M under normal glucose conditions. These effects were determined after incubation with a higher dose (4 mg/mL) of the LBP3M mixture, but relative pGSK-3 α / β at Tyr216/279 were decreased. In summary, treatment with the 4 mg/mL LBP3M mixture has protective effects on sperm motility upon exposure to excess iron and potentially acts as a glucose source, modulating the posttranslational signals of GSK-3 phosphorylation to promote capacitation.