中央研究院 生物化學研究所
中央研究院 生物化學研究所
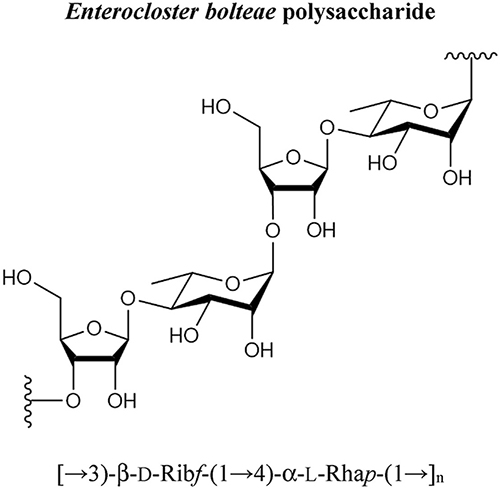
Enterocloster bolteae (formerly known as Clostridium bolteae) is a gastro-intestinal pathogenic bacterium often detected in the fecal microbiome of children in the autism spectrum. E. bolteae excretes metabolites that are thought to act as neurotoxins. This study is an update of our first E. bolteae investigation that discovered an immunogenic polysaccharide. Through a combination of chemical derivatizations/degradations, spectrometry and spectroscopy techniques, a polysaccharide composed of disaccharide repeating blocks comprised of 3-linked β-d-ribofuranose and 4-linked α-l-rhamnopyranose, [→3)-β-D-Ribf-(1 → 4)-α-L-Rhap-(1→]n, was identified. To confirm the structure, and to provide material for subsequent investigations, the chemical synthesis of a corresponding linker-equipped tetrasaccharide, β-D-Ribf-(1 → 4)-α-L-Rhap-(1 → 3)-β-D-Ribf-(1 → 4)-α-L-Rhap-(1→O(CH2)8N3, is also described. Research tools based on this immunogenic glycan structure can form the foundation for serotype classification, diagnostic/vaccine targets and clinical studies into the hypothesized role of E. bolteae in the onset/augmentation of autism related conditions in children.