中央研究院 生物化學研究所
中央研究院 生物化學研究所
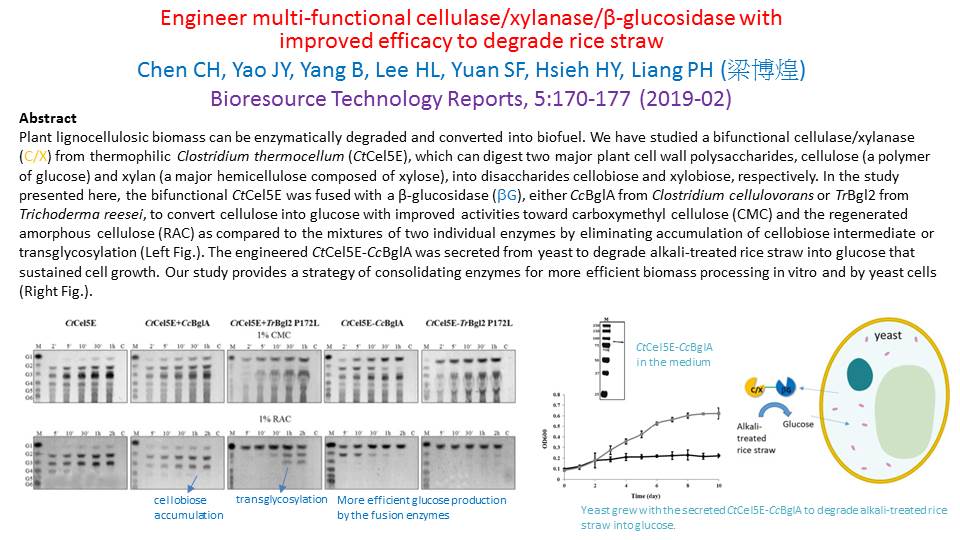
Plant lignocellulosic biomass can be enzymatically degraded and converted into biofuel. We have studied a bifunctional cellulase/xylanase from thermophilic Clostridium thermocellum (CtCel5E), which can digest two major plant cell wall polysaccharides, cellulose (a polymer of glucose) and xylan (a major hemicellulose composed of xylose), into disaccharides cellobiose and xylobiose, respectively. In the study presented here, the bifunctional CtCel5E was fused with a β-glucosidase from Clostridium cellulovorans (CcBglA) to convert cellulose into glucose with improved activities toward carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC), regenerated amorphous cellulose (RAC), and alkali-treated rice straw as compared to the mixture of two individual enzymes by eliminating accumulation of cellobiose intermediate. The engineered CtCel5E-CcBglA was secreted from yeast to degrade alkali-treated rice straw into glucose that sustained cell growth. Our study provides a strategy of consolidating enzymes for more efficient biomass processing in vitro and by yeast cells.