中央研究院 生物化學研究所
中央研究院 生物化學研究所
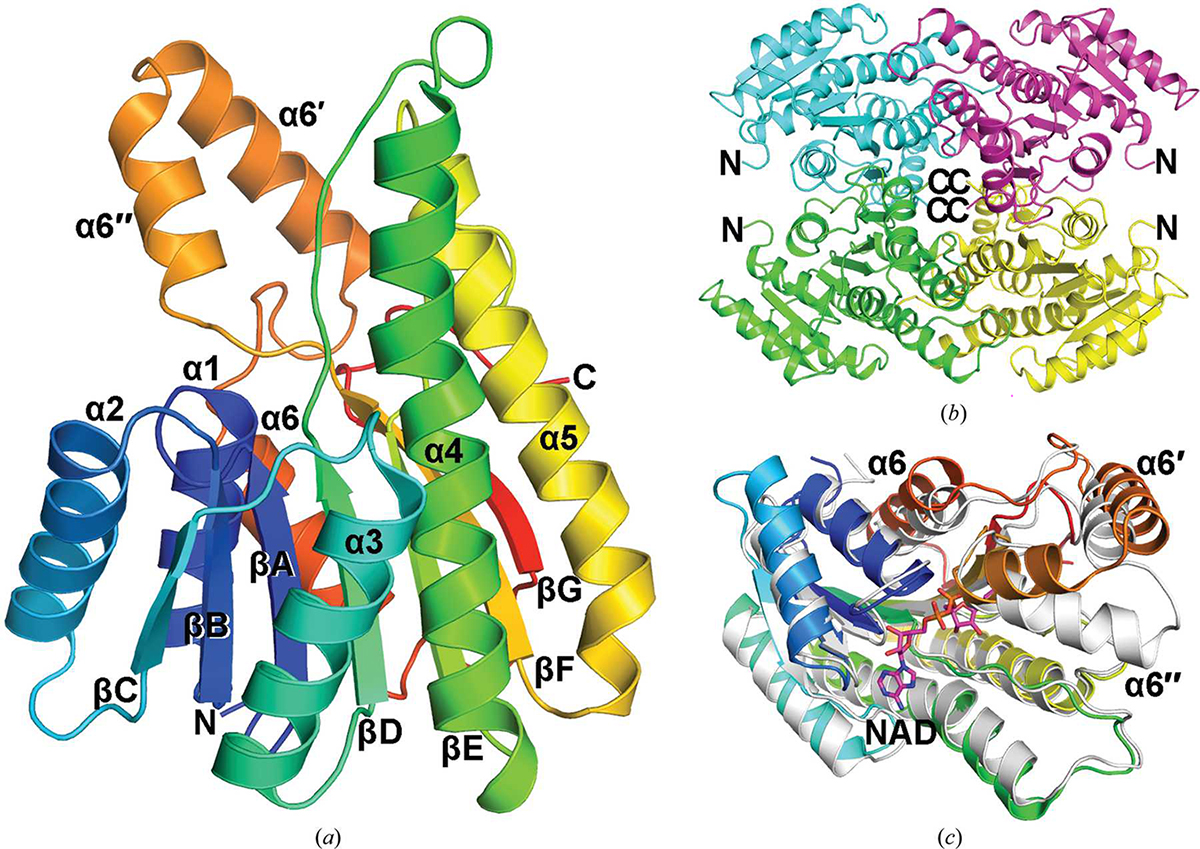
During the microbial degradation of borneol, a bicyclic plant monoterpene, it is first converted into camphor by borneol dehydrogenase (BDH) and then enters a known camphor-degradation pathway. Previously, a recombinant Pseudomonas BDH was found in inclusion bodies when expressed in Escherichia coli. After refolding, it was still unstable and was difficult to concentrate. Here, the protein-expression conditions were improved by changing the medium from lysogeny broth to Terrific Broth, yielding a soluble form of the enzyme with higher activity. The protein was crystallized and its 3D structure was determined by X-ray diffraction. Like other known homologues such as quinuclidinone reductase, the protein forms a tetramer with subunits containing Rossmann folds. Structural comparison revealed major differences in the C-terminal helices and the associated loops. It is likely that these regions contain the determinants for substrate recognition.