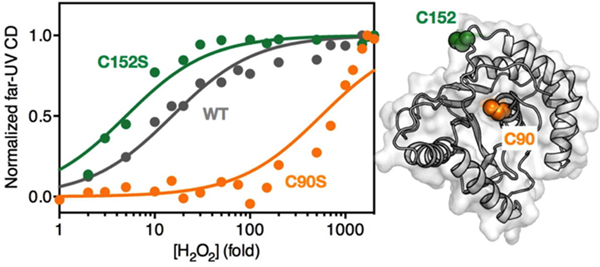
Redox-dependent inactivation of deubiquitinases (DUBs) is a critical factor for attenuating their DUB activity in response to cellular oxidative stress. Ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase isoform (UCH-L1) is an important DUB that is highly expressed in human neuronal cells and is implicated in a myriad of human diseases such as neurodegenerative diseases and cancer. Increasing evidence suggests an important role of UCH-L1 in redox regulation and the protection of neuronal cells from oxidative stress. In this study, we examined the molecular basis of how UCH-L1 responds to oxidation in a reversible manner. Using H2O2 as a model oxidant, we showed by mass spectrometry that a subset of methionine and cysteine residues, namely (M1, M6, M12, C90, and C152) were more susceptible to oxidation. Spectroscopic analysis showed that oxidation of C90 can lead to profound structural changes in addition to the loss of function. Importantly, we further demonstrated that C152, which is located at the substrate recognition cross-over loop, serves as a reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenger to protect catalytic C90 from oxidation under moderate oxidative conditions. Hydrogen-deuterium exchange mass spectrometry analysis provided detailed structural mapping of the destabilizing effect of H2O2-mediated oxidation, which resulted in global destabilization far beyond the oxidation sites. These perturbations may be responsible for irreversible aggregation when subject to prolonged oxidative stress.

 Institute of Biological Chemistry, Academia Sinica
Institute of Biological Chemistry, Academia Sinica