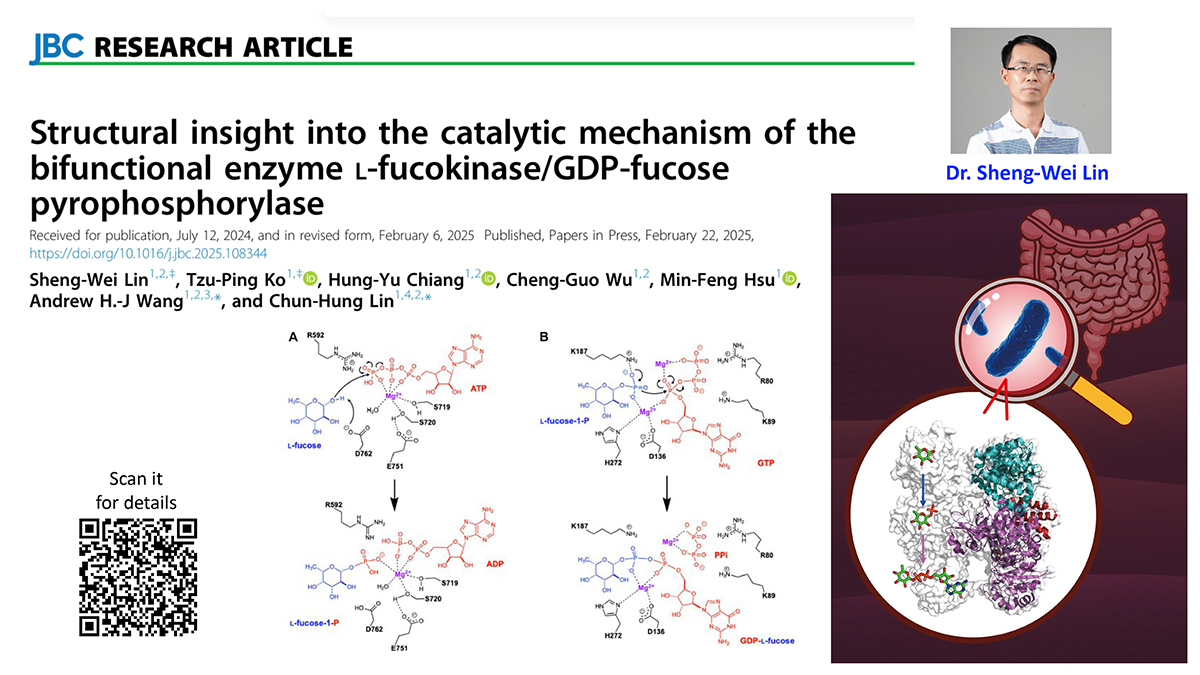
The bifunctional l-fucokinase/GDP-β-l-fucose pyrophosphorylase (FKP) from Bacteroides fragilis catalyzes the conversion from l-fucose to GDP-β-l-fucose. The reaction product, representing the activated form of l-fucose, is used by all l-fucosyltransferases to incorporate l-fucose. Herein, we report the first X-ray crystal structures of FKP in complex with substrate-product, leading to the dissection of both activity domains and corresponding catalytic mechanisms. The full-length FKP (FKP-FL, 949 amino acids) exists as a tetramer in solution, but the individually prepared N-terminal domain (FKP-NTD corresponding to the sequence 1-496, also containing a SUMO tag) and C-terminal domain (FKP-CTD, the sequence 519-949) form a monomer and a dimer, respectively. FKP-NTD has a single α/β domain and a β-helix-containing domain, whereas FKP-CTD folds into two α/β domains and the linker comprises three α-helices. The β-l-fucose-1-phosphate (fucose-1-P) and GTP bound separately to the active sites of fucokinase (located at FKP-CTD) and pyrophosphorylase (FKP-NTD), and a third nucleotide-binding site is adjacent to the β-helix (also in FKP-NTD). Furthermore, Asp762 was proposed to serve as the general base in the reaction of fucokinase, to deprotonate the C1-OH of fucose in the nucleophilic attack to γ-phosphate of ATP, resulting in the formation of fucose-1-P. At the same time, Arg592 and magnesium ion stabilize the developing negative charge in the leaving group (ADP). Subsequently, in the pyrophosphorylase-catalyzed reaction, the Lys187 side chain facilitates the nucleophilic attack of fucose-1-P toward GTP, leading to the formation of GDP-fucose.

 Institute of Biological Chemistry, Academia Sinica
Institute of Biological Chemistry, Academia Sinica